Knee Replacement
If your knee has been damaged by arthritis, a fracture, or other conditions, you can have severe pain with simple activities such as walking or getting in and out of a chair. Your knee may be stiff causing difficulty putting on your shoes and socks. You may even have pain while sitting or sleeping.
We have many conservative measures to relieve pain from arthritis such as injections, medications, PRP, and physical therapy. But if these are not adequate to relieve your pain, knee replacement may be the best option.
Knee replacement surgery is a safe and effective procedure that can relieve your pain, increase motion, and help you get back to enjoying normal, everyday activities.
We can even perform knee replacements as an outpatient if you meet the qualifications.
Knee replacement surgery is one of the most successful operations in all of medicine. It can return you to the life you want to live!
Anatomy
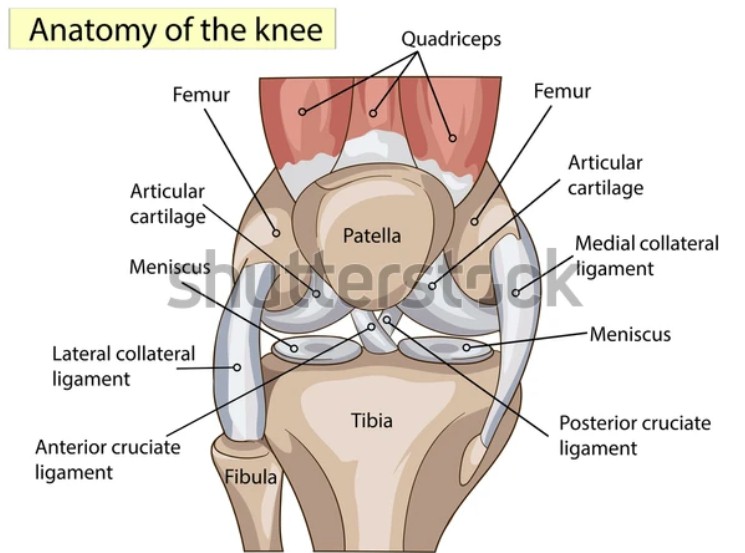
The knee is one of the body's largest joints. It is a complex hinge joint with three main articular surfaces between the femur (thighbone), tibia (shinbone), and patella (kneecap.)
The joint surface is covered with articular cartilage, a smooth tissue that cushions the ends of the bones and enables them to move easily. Arthritis occurs when this cartilage is damaged and wears away, leaving bare bone instead.
A thin tissue called the synovial membrane surrounds the knee joint. In a healthy knee, this membrane makes a small amount of fluid that lubricates the cartilage and eliminates almost all friction during knee movement.
Thick bands of tissue called ligaments connect the femur and tibia and provide stability to the joint. The meniscus is a c-shaped piece of firm cartilage that helps to cushion the knee joint. There is a medial and lateral meniscus in each knee. An arthritic knee will usually have extensive tearing of the menisci as well, but fixing those tears alone will not relieve the pain of arthritis.
Knee Replacement Surgery
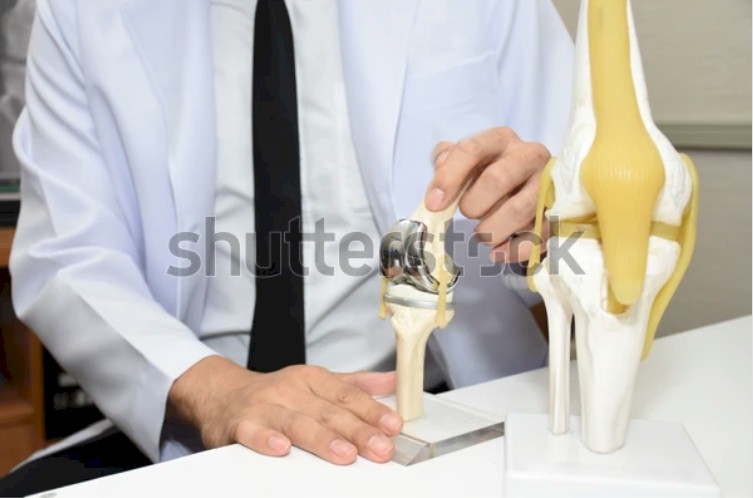
In a total knee replacement (also called total knee arthroplasty), the damaged bone and cartilage is removed and replaced with prosthetic components.
During a knee replacement, the ends of the bone are cut to remove the damaged surfaces. The menisci are removed and the ends of the bone are trimmed to shape for the new prosthetic components. Bone spurs are removed and certain ligaments may also have to be taken out.
The surfaces of the femur and tibia are replaced with metallic components. A plastic bearing is secured to the tibial tray, which allows for smooth gliding of the joint. The back of the kneecap is also usually resurfaced with a plastic button. Sometimes, some of these components my be coated in ceramic instead of the normal surgical steel. The components may be either cemented or press fit to secure them to the bone.
[IMAGE OF KNEE REPLACEMENT COMPONENTS]
Do you have to stay in the hospital after surgery?
Modern advances in surgical techniques mean shorter hospital stays than ever. If you are healthy and have good support at home, you may be a candidate to go home the same day as your surgery. But even if you stay overnight, most people are able to go home the next day.
For more information, you can read our article about Outpatient Joint Replacement HERE.
When is it time to get a knee replacement?
The decision to have knee replacement surgery should be a cooperative one made by you, your family, your primary care doctor, and your orthopaedic surgeon. It is important to consider your level of pain, diagnosis, other medical conditions, and effectiveness of conservative treatment options.
When is knee replacement recommended?
The people who benefit the most from knee replacement include those who have:
- Knee pain that limits everyday activities, such as walking or bending
- Knee pain that continues while resting, either day or night
- Stiffness in a knee that severely limits the ability to move or lift the leg
- Inadequate pain relief from anti-inflammatory drugs, physical therapy, or walking supports
Who is a candidate for knee replacement surgery?
Recommendations for surgery are based on a patient's pain and disability, not age. Most patients who undergo total knee replacement are age 50 to 80, but orthopaedic surgeons evaluate patients individually.
Total knee replacements have been performed successfully at all ages, from the but the younger you are, the more likely you are to need to wear out the replacement and need revision surgery.
Poorly controlled diabetes puts you at high risk for infection after surgery. And an infected joint replacement can put your life at risk or could require removal of the prosthetic joint. So, we require that your blood sugar be under good control before performing a knee replacement.
High BMI can also put you at significant risk for complications after surgery, so we evaluate these cases on an individual basis.
What are the risks of knee replacement?
The risks of joint replacement have been greatly reduced over the years. Improvements in the materials mean that modern replacements wear out much more slowly than before.
Improvements in surgical technique as well as the use of tranexamic acid (TXA) during surgery have greatly reduced bleeding and the possibility of transfusion after surgery.
Blood clots are always a risk after joint replacement, and you will need to be on blood thinners for 2-4 weeks after joint replacement surgery.
Other risks will be discussed by your surgeon before you make the decision to go forward with your joint replacement.
Realistic Expectations
An important factor in deciding whether to have knee replacement surgery is understanding what the procedure can and cannot do. Most people who undergo knee replacement surgery experience a dramatic reduction of knee pain and a significant improvement in their ability to perform the common activities of daily living.
If you only have pain with athletics, but are able to perform the rest of your daily activities without pain, you probably won’t experience much improvement from a joint replacement. We would recommend you alter your athletic activities instead and delay a knee replacement until the arthritis inhibits daily life instead.
With normal use and activity, the material between the head and the socket of every knee replacement implant begins to wear. Excessive activity or being overweight may speed up this normal wear and cause the knee replacement to loosen and become painful. Therefore, most surgeons advise against high-impact activities such as running, jumping, or other high-impact sports. If you have particular activities that you are looking forward to you should discuss them with your surgeon.
Realistic activities following total knee replacement include unlimited walking, swimming, golf, driving, hiking, biking, dancing, and other low-impact sports.
With appropriate activity modification, knee replacements can last for many years.
Surgeons Performing Knee Replacement
Dr. Richard Patterson
Dr. Thomas Courtney
Dr. Steven Pancio